The Importance of Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources
Resources are essential for sustaining life and driving economic activities. They can be broadly categorized into renewable and non-renewable resources, each playing a crucial role in our daily lives.
Renewable Resources
Renewable resources are those that can be replenished naturally over time. They are sustainable and have minimal impact on the environment. Examples of renewable resources include:
- Solar energy: Harnessing sunlight to generate electricity through solar panels.
- Wind energy: Utilizing wind turbines to convert wind power into electricity.
- Hydropower: Generating electricity from flowing water in rivers or dams.
- Biomass: Using organic materials like wood, crop residues, and biofuels for energy production.
- Geothermal energy: Tapping into heat from the Earth’s core for heating and electricity generation.
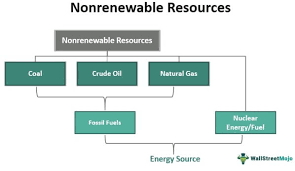
Non-Renewable Resources
Non-renewable resources are finite and cannot be easily replaced once depleted. Their extraction and consumption often have significant environmental impacts. Examples of non-renewable resources include:
- Petroleum: Used for fuel, plastics, and various industrial applications.
- Natural gas: A fossil fuel used for heating, cooking, and electricity generation.
- Coal: A major source of electricity generation in many countries.
- Uranium: Mined for nuclear power generation in nuclear reactors.
- Metal ores: Including iron ore, copper, gold, and silver used in manufacturing and construction.
It is vital to balance the use of renewable and non-renewable resources to ensure a sustainable future for generations to come. Transitioning towards greater reliance on renewable resources can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mitigate climate change, and preserve natural ecosystems.
By understanding the significance of both types of resources and making informed choices about their utilization, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient world for ourselves and future generations.
9 Key Examples of Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy Resources: Harnessing Nature and Tapping into Fossil Fuels
- 1. Use solar panels to harness energy from the sun.
- 2. Install wind turbines to generate electricity from wind power.
- 3. Utilize hydropower by building dams on rivers and streams.
- 8. Explore the use of tidal power as a renewable source of energy.
- Coal
- A fossil fuel formed from decayed plant matter over millions of years.
- Petroleum (Oil)
- A liquid fossil fuel extracted from underground reservoirs.
- Natural Gas
1. Use solar panels to harness energy from the sun.
One effective way to utilize renewable resources is by installing solar panels to harness energy from the sun. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, providing a clean and sustainable source of power for homes, businesses, and communities. By tapping into this abundant and renewable resource, we can reduce our reliance on non-renewable sources like fossil fuels and decrease our carbon footprint. Embracing solar energy not only helps to mitigate climate change but also promotes energy independence and environmental stewardship for a brighter and more sustainable future.
2. Install wind turbines to generate electricity from wind power.
Installing wind turbines to generate electricity from wind power is a sustainable way to harness renewable energy. By utilizing the natural force of the wind, we can produce clean electricity without depleting non-renewable resources like fossil fuels. Wind power is a reliable and environmentally friendly alternative that helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. Embracing technologies like wind turbines not only promotes energy independence but also contributes to a greener and more sustainable future for our planet.
3. Utilize hydropower by building dams on rivers and streams.
Utilizing hydropower by constructing dams on rivers and streams is an example of harnessing a renewable resource to generate electricity. Hydropower is a clean and sustainable energy source that relies on the natural flow of water to produce power. By strategically building dams, we can capture the energy of flowing water and convert it into electricity, reducing our dependence on non-renewable resources like coal or natural gas. However, it’s important to consider the environmental impact of dam construction on local ecosystems and communities, ensuring that sustainable practices are implemented to minimize any negative consequences.
8. Explore the use of tidal power as a renewable source of energy.
Exploring the use of tidal power as a renewable source of energy is a promising avenue towards sustainable energy production. Tidal power harnesses the natural ebb and flow of ocean tides to generate electricity, offering a reliable and consistent source of renewable energy. By tapping into this abundant resource, we can reduce our reliance on non-renewable fossil fuels and decrease carbon emissions, contributing to a cleaner and greener energy landscape. Embracing tidal power technology showcases our commitment to innovative solutions that prioritize environmental conservation and long-term sustainability.
Coal
Coal is a prominent example of a non-renewable resource that has been a cornerstone of energy production for centuries. Mined from the earth, coal has historically played a vital role in powering industries, generating electricity, and heating homes. However, its extensive use has raised concerns due to its environmental impact, including air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. As we seek to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, the importance of reducing our reliance on coal and shifting towards renewable alternatives like solar, wind, and hydropower becomes increasingly apparent for a greener future.
A fossil fuel formed from decayed plant matter over millions of years.
Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are prime examples of non-renewable resources that have been formed from the decomposition of plant and organic matter over millions of years. These ancient energy sources have powered industrial revolutions and modern societies but come at a cost to the environment due to their finite nature and contribution to climate change. Transitioning towards cleaner, renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power is crucial for reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and building a sustainable future for generations to come.
Petroleum (Oil)
Petroleum, also known as oil, is a prominent example of a non-renewable resource that plays a critical role in various aspects of modern life. Extracted from deep within the Earth’s crust, petroleum is used as a primary source of fuel for transportation, heating, and electricity generation. Additionally, petroleum serves as a key ingredient in the production of plastics, chemicals, and lubricants. However, the finite nature of petroleum reserves and the environmental impact of its extraction and consumption underscore the importance of transitioning towards renewable energy sources to reduce our dependence on this valuable but limited resource.
A liquid fossil fuel extracted from underground reservoirs.
One common example of a non-renewable resource is petroleum, a liquid fossil fuel extracted from underground reservoirs. Petroleum, also known as crude oil, is a vital energy source used for transportation, heating, and various industrial applications. Its finite nature and environmental impact highlight the importance of transitioning towards renewable energy sources to reduce our reliance on non-renewable resources like petroleum and mitigate the associated environmental challenges.
Natural Gas
Natural gas is a widely used non-renewable resource that plays a significant role in meeting energy demands worldwide. It is primarily used for heating, cooking, and electricity generation due to its relatively clean combustion compared to other fossil fuels. However, the extraction and consumption of natural gas can have environmental consequences, such as methane emissions during production and transportation. As we strive for a more sustainable future, exploring alternative energy sources like renewables alongside natural gas can help reduce carbon emissions and lessen our impact on the environment.