Community Resilience: Building Strength in the Face of Challenges
In an ever-changing world, community resilience has become an essential concept for individuals, neighborhoods, and societies. It refers to the ability of a community to withstand and recover from shocks, stresses, and adversities while maintaining its core functions, structures, and values. Community resilience goes beyond mere survival; it encompasses the capacity to adapt, learn, and thrive in the face of challenges.
A resilient community is one that is prepared for a variety of disruptions, whether they be natural disasters like hurricanes or earthquakes, economic downturns, social unrest, or environmental changes. It is a community that fosters strong social connections and collaboration among its members. These connections create a robust support network that can provide assistance during difficult times.
One key aspect of community resilience is the presence of diverse skills and resources within the community. When individuals possess a range of abilities and knowledge, they can contribute their expertise when needed most. This diversity helps communities respond effectively to crises by drawing on various perspectives and problem-solving approaches.
Education plays a crucial role in building community resilience. By providing residents with information about potential risks and teaching practical skills such as first aid or disaster preparedness, communities empower individuals to take action when faced with adversity. Education also promotes awareness of sustainable practices and encourages environmentally friendly behaviors that enhance long-term resilience.
Furthermore, community engagement is vital for fostering resilience. When people feel connected to their neighbors and actively participate in local initiatives, they develop a sense of belonging and shared responsibility for their community’s well-being. This involvement strengthens social cohesion and cooperation during challenging times.
Investing in infrastructure that supports resilience is another important aspect of building strong communities. This includes developing efficient transportation systems, reliable communication networks, sustainable energy sources, accessible healthcare facilities, and well-designed public spaces. By creating infrastructure that can withstand shocks and disruptions while facilitating recovery efforts, communities are better equipped to handle crises effectively.
In addition to physical infrastructure, community resilience also relies on the presence of robust governance structures and effective leadership. Transparent decision-making processes and inclusive policies ensure that the community’s needs and voices are heard. Strong leadership fosters trust, inspires collective action, and enables communities to navigate complex challenges successfully.
Lastly, collaboration between communities, organizations, and government agencies is essential for building resilience at a larger scale. Sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices allows communities to learn from one another’s experiences and leverage collective strengths. Collaboration also enables the development of coordinated response plans that can be activated swiftly during emergencies.
Community resilience is not a destination but an ongoing journey. It requires continuous efforts to strengthen social bonds, enhance skills and knowledge, invest in infrastructure, engage residents actively, and promote collaboration. By prioritizing resilience-building measures, communities can ensure a safer, more sustainable future for their members.
In conclusion, community resilience is about more than just surviving adversity; it is about thriving in the face of challenges. By fostering strong social connections, investing in education and infrastructure, promoting community engagement, nurturing effective leadership, and fostering collaboration between different stakeholders, communities can build resilience that enables them to adapt and flourish even in times of crisis. Together we can create a world where communities are empowered to face any challenge head-on with strength, unity, and determination.
8 Frequently Asked Questions About Community Resilience: A Guide to Understanding and Strengthening Community Resilience
- What is community resilience?
- How can I help build community resilience?
- What are the benefits of a resilient community?
- How do you measure community resilience?
- What strategies can be used to increase community resilience?
- How does climate change affect local communities’ ability to be resilient?
- How can we create social networks and support systems that promote community resilience?
- What resources are available to help my local community become more resilient?
What is community resilience?
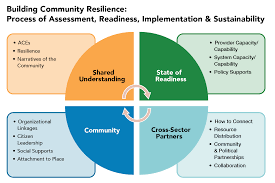
Community resilience refers to the ability of a community to withstand and recover from shocks, stresses, and adversities while maintaining its core functions, structures, and values. It is the capacity of a community to bounce back and adapt in the face of challenges, whether they are natural disasters, economic downturns, social disruptions, or environmental changes.
A resilient community is not only able to survive during difficult times but also to thrive and grow stronger as a result. It is characterized by strong social connections, collaboration among its members, diverse skills and resources, effective leadership, and robust infrastructure. Community resilience goes beyond individual preparedness; it focuses on building collective strength and fostering a sense of shared responsibility for the well-being of the community as a whole.
Key elements of community resilience include:
- Social Connections: Strong social networks and relationships within a community provide support during crises. They enable people to come together, share resources, provide emotional support, and collectively address challenges.
- Diverse Skills and Resources: A resilient community possesses a wide range of skills and resources among its members. This diversity allows for effective problem-solving during times of adversity by drawing on various perspectives and expertise.
- Education and Awareness: Community resilience is enhanced through education that provides individuals with knowledge about potential risks, disaster preparedness strategies, sustainable practices, and other relevant information.
- Infrastructure: Resilient communities invest in infrastructure that can withstand shocks or disruptions while facilitating recovery efforts. This includes reliable transportation systems, communication networks, healthcare facilities, energy sources, housing structures designed for resilience, and well-designed public spaces.
- Effective Leadership: Strong leadership plays a crucial role in guiding communities through challenging times. Transparent decision-making processes that consider diverse perspectives help build trust among community members.
- Community Engagement: Active participation by residents in local initiatives fosters a sense of belonging and shared responsibility for the well-being of the community. Engaged communities are better equipped to respond collectively during crises.
- Collaboration: Building resilience requires collaboration between communities, organizations, and government agencies. Sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices enhances collective strength and enables coordinated response plans during emergencies.
Community resilience is an ongoing process that requires continuous efforts to strengthen social bonds, enhance skills and knowledge, invest in infrastructure, engage residents actively, nurture effective leadership, and promote collaboration. By prioritizing resilience-building measures, communities can better prepare for and adapt to challenges, ultimately creating a more sustainable and thriving future for their members.
How can I help build community resilience?
Building community resilience is a collective effort that requires the involvement and commitment of individuals like yourself. Here are some ways you can contribute to building community resilience:
- Get involved: Engage with your local community organizations, neighborhood associations, or volunteer groups. Participate in community events, meetings, and initiatives. By actively participating, you can contribute your skills, ideas, and energy to strengthen the resilience of your community.
- Foster social connections: Build relationships with your neighbors and fellow community members. Organize neighborhood gatherings or events that promote social interaction and collaboration. Strong social connections create a support network that can provide assistance during challenging times.
- Share knowledge and skills: Offer to teach or share your expertise with others in your community. Conduct workshops or training sessions on topics such as disaster preparedness, sustainable living practices, gardening, or first aid. Sharing knowledge empowers individuals to take proactive measures and builds collective resilience.
- Support local businesses: Patronize local businesses and encourage others to do the same. Local businesses are often the backbone of a community’s economy and play a vital role in its resilience. Supporting them helps create economic stability within the community.
- Volunteer for emergency response efforts: Join local emergency response teams or organizations that provide disaster relief services. Volunteer your time and skills during emergencies or participate in drills and exercises to enhance preparedness within your community.
- Promote sustainable practices: Encourage environmentally friendly behaviors within your community by promoting recycling, energy conservation, water conservation, and sustainable transportation options. These practices contribute to long-term resilience by reducing environmental impact and resource consumption.
- Advocate for resilient infrastructure: Stay informed about infrastructure development plans in your area and advocate for resilient design principles that consider potential risks and incorporate measures for adaptation and recovery from shocks or disasters.
- Support inclusive policies: Stay engaged with local governance processes by attending council meetings or participating in public consultations on issues related to resilience-building. Advocate for inclusive policies that address the needs of all community members, especially vulnerable populations.
- Prepare yourself and your family: Take steps to ensure your own personal preparedness for emergencies. Create an emergency kit, develop a family communication plan, and stay informed about potential risks in your area. By being prepared, you can contribute to a more resilient community.
- Spread awareness: Share information about community resilience with your friends, family, and neighbors. Use social media platforms or organize educational events to raise awareness about the importance of building resilience and provide practical tips for individuals to get involved.
Remember that building community resilience is an ongoing process that requires sustained effort and collaboration. By taking these actions, you can make a meaningful contribution to creating a stronger, more resilient community for everyone.
What are the benefits of a resilient community?
A resilient community offers numerous benefits that contribute to the overall well-being and sustainability of its members. Here are some key advantages of a resilient community:
- Enhanced Preparedness: A resilient community is better equipped to handle and respond to various types of challenges, such as natural disasters, economic downturns, or social disruptions. By being prepared, communities can minimize the impact of these events and recover more quickly.
- Reduced Vulnerability: Resilient communities actively identify and address vulnerabilities within their systems and structures. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks and reduces the potential for harm during crises. By strengthening infrastructure, improving communication networks, and implementing safety measures, communities become less susceptible to damage.
- Improved Social Connections: Building resilience fosters strong social connections among community members. When individuals feel connected to their neighbors and have a sense of belonging, they are more likely to support one another during difficult times. These social bonds create a network of care and assistance that enhances overall well-being.
- Increased Adaptability: Resilient communities possess the ability to adapt to changing circumstances effectively. They can adjust their strategies, policies, and practices in response to new challenges or emerging trends. This adaptability allows communities to stay ahead of potential risks and seize opportunities for growth and development.
- Economic Stability: Community resilience is closely tied to economic stability. By investing in sustainable practices, diversifying local economies, promoting entrepreneurship, and supporting small businesses, resilient communities can better withstand economic shocks or downturns. This stability helps maintain employment opportunities and improves the overall quality of life for residents.
- Environmental Sustainability: Resilient communities prioritize environmental stewardship by adopting sustainable practices such as renewable energy sources, waste reduction strategies, water conservation efforts, and green infrastructure development. By minimizing their ecological footprint, these communities contribute to long-term environmental sustainability.
- Healthier Communities: Resilience-building measures often promote physical and mental well-being within communities. By investing in healthcare facilities, promoting access to nutritious food, creating safe public spaces, and supporting active lifestyles, resilient communities foster healthier populations. This leads to reduced healthcare costs and improved overall quality of life.
- Collective Empowerment: Building resilience empowers individuals and communities to take control of their own destiny. By equipping residents with knowledge, skills, and resources, communities can actively participate in decision-making processes and shape their future. This empowerment strengthens community cohesion and fosters a sense of ownership over shared goals.
- Improved Crisis Response: Resilient communities have well-established response plans and systems in place to address crises effectively. By having clear communication channels, trained emergency responders, and coordinated efforts among various stakeholders, these communities can respond swiftly during emergencies, potentially saving lives and minimizing damage.
- Long-Term Sustainability: Ultimately, the benefits of a resilient community extend beyond immediate crises. By prioritizing resilience-building measures, communities create a foundation for long-term sustainability. They can adapt to changing circumstances while maintaining their core values and functions over time.
In summary, a resilient community offers numerous advantages ranging from enhanced preparedness and reduced vulnerability to improved social connections, economic stability, environmental sustainability, collective empowerment, improved crisis response capabilities, and long-term sustainability. By investing in resilience-building measures, communities can thrive even in the face of adversity while ensuring the well-being of their members for generations to come.
How do you measure community resilience?
Measuring community resilience is a complex task that involves assessing various dimensions and indicators. While there is no universally agreed-upon method, several approaches and frameworks have been developed to evaluate community resilience. Here are some common methods used to measure community resilience:
- Surveys and Interviews: Conducting surveys and interviews with community members can provide valuable insights into their perceptions of resilience. Questions can be designed to assess factors such as social cohesion, trust, sense of belonging, preparedness for disasters, access to resources, and overall well-being.
- Indicators and Metrics: Developing specific indicators and metrics allows for the quantification of resilience-related factors. These can include variables like infrastructure quality, economic stability, healthcare accessibility, educational attainment, environmental sustainability measures, crime rates, or unemployment levels. By tracking these indicators over time, changes in community resilience can be observed.
- Resilience Indexes: Some organizations have created composite indexes that combine multiple indicators to measure overall community resilience. These indexes often consider aspects such as social capital (community networks and connections), economic stability (employment rates and income inequality), infrastructure quality (transportation systems and utilities), environmental sustainability (natural resource management), and governance effectiveness.
- Case Studies: In-depth case studies of specific communities can provide a qualitative understanding of their resilience. Researchers analyze how communities have responded to past shocks or stresses by examining their adaptive capacity, recovery processes, collaboration efforts, leadership effectiveness, and the ability to learn from experiences.
- Simulation Models: Computer-based simulation models can help assess the impact of various shocks or stresses on a community’s functioning over time. These models consider factors like population dynamics, infrastructure systems, economic interdependencies, social networks, and response strategies. By simulating different scenarios and analyzing outcomes, researchers can gain insights into a community’s ability to bounce back from disruptions.
It is important to note that measuring community resilience is not an exact science due to its complex and multifaceted nature. Different approaches may yield varied results, and it is crucial to consider the specific context and goals of the assessment. The combination of quantitative and qualitative methods, along with community engagement, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of community resilience.
What strategies can be used to increase community resilience?
Increasing community resilience requires a multifaceted approach that involves various strategies and initiatives. Here are some key strategies that can be employed to enhance community resilience:
- Foster social connections and networks: Encourage community members to build strong relationships with their neighbors, local organizations, and institutions. Strengthening social bonds creates a support network that can provide assistance during times of crisis.
- Promote community engagement: Encourage residents to actively participate in local initiatives, events, and decision-making processes. Engaged communities have a stronger sense of ownership, shared responsibility, and collective action.
- Enhance education and awareness: Provide educational programs that equip individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to prepare for and respond to emergencies. Educate residents about potential risks, disaster preparedness, sustainable practices, and environmental conservation.
- Develop inclusive governance structures: Establish transparent decision-making processes that involve diverse voices within the community. Ensure that policies consider the needs of all residents, particularly vulnerable populations.
- Invest in infrastructure: Develop resilient infrastructure systems such as reliable transportation networks, communication systems, healthcare facilities, renewable energy sources, and sustainable water management systems. Infrastructure should be designed to withstand shocks and facilitate quick recovery.
- Support local businesses: Encourage economic diversity by supporting local businesses and promoting entrepreneurship within the community. A diverse economy is more resilient to economic downturns.
- Preserve natural resources: Protect and restore natural ecosystems within the community as they provide numerous benefits such as flood mitigation, clean air, water filtration, and biodiversity conservation.
- Build capacity for self-sufficiency: Encourage self-reliance by promoting skills development in areas such as gardening, food production, renewable energy generation, first aid training, and basic construction techniques.
- Establish effective communication channels: Develop reliable communication networks that can disseminate information quickly during emergencies or crises. This includes utilizing various mediums such as social media platforms or emergency alert systems.
- Foster collaboration and partnerships: Encourage collaboration between community members, local organizations, government agencies, and neighboring communities. Sharing resources, knowledge, and best practices enhances collective resilience.
- Conduct regular risk assessments: Identify potential hazards and vulnerabilities within the community through comprehensive risk assessments. This information can guide preparedness efforts and help prioritize resilience-building initiatives.
- Plan for long-term recovery: Develop comprehensive recovery plans that address the physical, emotional, and economic well-being of the community following a crisis. Consider long-term sustainability and rebuilding efforts.
By implementing these strategies, communities can enhance their resilience to various challenges and improve their ability to withstand shocks while maintaining their core functions, structures, and values. Remember that building resilience is an ongoing process that requires continuous effort, adaptability, and collaboration among community members.
How does climate change affect local communities’ ability to be resilient?
Climate change poses significant challenges to the resilience of local communities. Its impacts, such as rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, sea-level rise, and increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, can have far-reaching consequences for community well-being and their ability to withstand and recover from shocks and stresses. Here are some ways in which climate change affects local communities’ ability to be resilient:
- Increased exposure to natural hazards: Climate change amplifies the risks associated with natural hazards like hurricanes, floods, droughts, and wildfires. These events can cause extensive damage to infrastructure, homes, and livelihoods, disrupting community functioning and straining resources.
- Water resource availability: Changes in precipitation patterns affect water availability for communities. Droughts can lead to water scarcity, impacting agriculture, drinking water supplies, and industrial activities. Conversely, intense rainfall events can overwhelm drainage systems, leading to flooding and water contamination.
- Food security: Climate change impacts agricultural productivity through altered growing seasons, pests and diseases outbreaks, soil degradation, and water scarcity. These factors can reduce crop yields and disrupt food supply chains, potentially compromising food security within local communities.
- Health impacts: Climate change contributes to the spread of vector-borne diseases like malaria or dengue fever as changing temperatures create more favorable conditions for disease-carrying organisms. Heatwaves also pose health risks for vulnerable populations such as the elderly or those with pre-existing medical conditions.
- Displacement and migration: Rising sea levels and increased vulnerability to extreme weather events can lead to forced displacement of communities living in low-lying coastal areas or regions prone to flooding or erosion. This displacement can strain receiving communities’ resources while also disrupting social networks.
- Economic implications: Climate-related disruptions impact local economies by damaging infrastructure (e.g., roads or power grids), reducing productivity in sectors like agriculture or tourism, increasing insurance costs due to higher risks, or affecting supply chains through extreme weather events.
- Social cohesion and community well-being: Climate change impacts can generate social stress and strain community relationships. Disruptions to livelihoods, displacement, or resource scarcity can lead to increased competition and conflicts within communities, potentially undermining social cohesion.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that combines mitigation efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adaptation strategies to enhance resilience. Local communities can take actions such as implementing sustainable land and water management practices, diversifying livelihoods, developing early warning systems, improving infrastructure resilience, promoting community-based disaster preparedness plans, and integrating climate considerations into urban planning processes.
Moreover, collaboration between local communities, governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and other stakeholders is crucial for sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices. By working together at all levels, communities can enhance their ability to adapt to the changing climate while maintaining their core functions and values.
How can we create social networks and support systems that promote community resilience?
Creating social networks and support systems that promote community resilience requires intentional efforts to foster connections, collaboration, and mutual support among community members. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Encourage Community Engagement: Actively involve residents in community initiatives, decision-making processes, and problem-solving activities. Provide platforms for open dialogue and encourage participation in local events, workshops, or town hall meetings.
- Foster Strong Social Connections: Create opportunities for people to connect and build relationships within the community. This can be done through social gatherings, neighborhood associations, community gardens, or volunteer projects. Encourage residents to get to know their neighbors and promote a sense of belonging.
- Establish Communication Channels: Develop reliable communication channels that allow for the timely dissemination of information during emergencies or crises. This can include social media platforms, community newsletters, or localized alert systems. Ensure that communication methods are accessible to all members of the community.
- Facilitate Skill Sharing: Encourage residents to share their skills and expertise with others in the community through workshops or skill-sharing events. This can range from teaching basic first aid techniques to sharing knowledge about sustainable gardening practices or energy-efficient technologies.
- Promote Mutual Aid Networks: Encourage the formation of mutual aid networks where community members can provide support to one another during times of need. These networks can include services like meal delivery for the elderly, childcare assistance, or neighborly check-ins during emergencies.
- Provide Education and Training: Offer educational programs that focus on disaster preparedness, resilience-building practices, sustainable living techniques, or other relevant topics. Empower residents with knowledge and practical skills that enable them to respond effectively in times of crisis.
- Support Local Businesses and Organizations: Foster a strong local economy by supporting small businesses and organizations within the community. Collaborate with local entrepreneurs and nonprofits to develop initiatives that enhance resilience while promoting economic growth.
- Establish Community Resource Centers: Create physical spaces where residents can access information, resources, and support during emergencies. These centers can serve as hubs for distributing supplies, coordinating volunteer efforts, or providing counseling services.
- Collaborate with Existing Networks: Identify and collaborate with existing community organizations, faith-based groups, schools, or local government agencies. By working together, you can leverage their expertise and resources to strengthen community resilience efforts.
- Celebrate Success Stories: Highlight and celebrate examples of community resilience to inspire others. Share success stories through newsletters, websites, or local media outlets to promote a sense of pride and motivation within the community.
Remember that building social networks and support systems takes time and effort. It requires ongoing engagement and a commitment to inclusivity and collaboration. By implementing these strategies, communities can create a strong foundation for resilience while fostering a sense of unity and shared responsibility among its members.
What resources are available to help my local community become more resilient?
There are several resources available to help your local community become more resilient. Here are a few examples:
- Government and Nonprofit Organizations: Local government agencies and nonprofit organizations often provide resources and support for community resilience initiatives. They may offer funding opportunities, educational programs, workshops, and guidance on disaster preparedness, sustainable practices, and community development.
- Community Resilience Assessments: Many organizations offer tools and frameworks to assess the resilience of communities. These assessments can help identify strengths, vulnerabilities, and areas for improvement. They provide valuable insights into where resources should be directed and how to prioritize resilience-building efforts.
- Emergency Management Agencies: Local emergency management agencies can provide valuable information on disaster preparedness, response plans, and recovery strategies specific to your area. They often conduct workshops or training sessions on topics such as first aid, emergency communication, evacuation procedures, and shelter management.
- Extension Services: Cooperative Extension Services offered by universities provide research-based information and resources for various aspects of community resilience. They cover topics such as agriculture, natural resource management, sustainable practices, nutrition education, youth development programs, and more.
- Community Organizations: Look for local grassroots organizations or community groups that focus on sustainability, environmental conservation, or disaster preparedness. These organizations often organize events like workshops or seminars to educate residents on resilience-building strategies specific to your region.
- Online Resources: Numerous websites offer valuable information on community resilience strategies. The websites of government agencies like FEMA (Federal Emergency Management Agency) or NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) provide guidance on disaster preparedness plans tailored to different hazards such as floods, hurricanes, wildfires, etc.
- Networking Events: Attend local networking events related to sustainability or community development where you can connect with like-minded individuals who share an interest in building resilient communities. These events can be a great opportunity to exchange ideas, learn from others’ experiences, and find potential collaborators for resilience projects.
- Community Grants and Funding: Research available grants and funding opportunities that specifically support community resilience initiatives. Local foundations, government agencies, or corporate social responsibility programs often provide financial resources for projects aimed at enhancing community resilience.
Remember, building community resilience is a collective effort that requires collaboration and engagement from various stakeholders. By leveraging the resources available to you, you can take significant steps towards creating a more resilient and sustainable future for your local community.