The Importance of Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources
Resources are essential for sustaining life on Earth. They can be broadly categorized into two main types: renewable and nonrenewable resources. Understanding the differences between these two types is crucial for managing our planet’s resources sustainably.
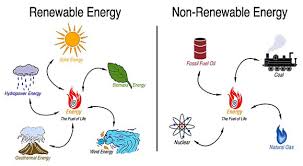
Renewable Resources
Renewable resources are those that can be replenished naturally over time. Examples include sunlight, wind, water, and biomass. These resources are abundant and have the potential to be used indefinitely without depleting them. Harnessing renewable resources for energy production, such as solar panels and wind turbines, is vital for reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
Nonrenewable Resources
In contrast, nonrenewable resources are finite and cannot be replenished within a human lifetime. Fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are prime examples of nonrenewable resources that took millions of years to form. Once these resources are depleted, they cannot be replaced. Over-reliance on nonrenewable resources not only leads to environmental degradation but also poses a threat to future generations’ well-being.
The Need for Sustainable Resource Management
As the global population grows and industrial activities increase, the demand for both renewable and nonrenewable resources continues to rise. It is imperative that we adopt sustainable practices to ensure the responsible use of resources for current and future generations.
By investing in renewable energy sources, promoting recycling programs, and implementing conservation measures, we can reduce our impact on the environment and preserve valuable resources for years to come.
Conclusion
Renewable and nonrenewable resources play a significant role in shaping our world’s sustainability. Embracing renewable alternatives while minimizing our dependence on nonrenewable sources is key to safeguarding the planet’s ecosystems and securing a sustainable future for all.
Understanding Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources: Frequently Asked Questions
- What are renewable resources?
- What are examples of renewable resources?
- How do renewable resources differ from nonrenewable resources?
- Why is it important to use renewable resources?
- What are nonrenewable resources?
- What are examples of nonrenewable resources?
- How do we deplete nonrenewable resources?
- What are the environmental impacts of using nonrenewable resources?
- How can individuals and communities transition to using more renewable resources?
What are renewable resources?
Renewable resources are natural sources of energy or materials that can be naturally replenished or regenerated within a human lifetime. Examples of renewable resources include sunlight, wind, water, and biomass. These resources are abundant and sustainable, meaning they can be utilized without the risk of depletion. Harnessing renewable resources for energy production is crucial for reducing our dependence on finite fossil fuels and mitigating the impacts of climate change. By tapping into the power of renewable resources, we can create a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future for generations to come.
What are examples of renewable resources?
Renewable resources are abundant and sustainable sources of energy that can be naturally replenished over time. Examples of renewable resources include sunlight, wind, water (hydroelectric power), biomass (organic materials like wood and crop residues), and geothermal energy. These resources offer a clean and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels, making them essential components in the transition to a more sustainable energy future. By harnessing the power of renewable resources, we can reduce our carbon footprint, combat climate change, and ensure a greener planet for future generations.
How do renewable resources differ from nonrenewable resources?
Renewable resources differ from nonrenewable resources in their ability to be naturally replenished over time. Renewable resources, such as sunlight, wind, and water, are abundant and can be used continuously without running out. In contrast, nonrenewable resources like fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) are finite and took millions of years to form. Once nonrenewable resources are depleted, they cannot be replaced within a human lifespan. This distinction highlights the importance of transitioning towards sustainable practices that prioritize the utilization of renewable resources to reduce environmental impact and ensure long-term resource availability for future generations.
Why is it important to use renewable resources?
It is crucial to use renewable resources due to their sustainable nature and positive environmental impact. Renewable resources, such as solar and wind energy, are abundant and can be replenished naturally. By harnessing renewable sources for energy production, we reduce our reliance on finite nonrenewable resources like fossil fuels, which contribute to climate change and environmental degradation. Utilizing renewable resources helps mitigate these negative effects, promotes energy independence, and supports a cleaner, greener future for generations to come.
What are nonrenewable resources?
Nonrenewable resources are finite natural substances that cannot be replaced within a human timescale once they are depleted. Examples of nonrenewable resources include fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, as well as minerals like copper and iron ore. These resources took millions of years to form through geological processes and extraction rates far exceed their replenishment rates. As such, nonrenewable resources are considered scarce and unsustainable in the long term if not managed responsibly. It is crucial for societies to transition towards renewable alternatives to reduce their reliance on nonrenewable resources and mitigate environmental impacts associated with their extraction and consumption.
What are examples of nonrenewable resources?
Nonrenewable resources are finite natural substances that cannot be replaced within a human lifetime. Examples of nonrenewable resources include fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, which formed over millions of years from organic matter. Other examples include minerals like copper, iron ore, and uranium, which are extracted from the Earth’s crust and have limited reserves. The extraction and consumption of nonrenewable resources have significant environmental impacts and contribute to climate change. It is essential to explore alternative energy sources and promote sustainable practices to reduce our reliance on nonrenewable resources for a more sustainable future.
How do we deplete nonrenewable resources?
Nonrenewable resources are depleted through extraction and consumption at a rate that far exceeds their natural replenishment process. Human activities such as mining, drilling, and burning fossil fuels accelerate the depletion of nonrenewable resources like coal, oil, and natural gas. As these resources are finite and take millions of years to form, their extraction for energy production, manufacturing, and other purposes leads to their rapid depletion. Without careful management and transition to sustainable alternatives, the overexploitation of nonrenewable resources can have detrimental effects on the environment, economy, and future generations.
What are the environmental impacts of using nonrenewable resources?
The environmental impacts of using nonrenewable resources are profound and far-reaching. The extraction, processing, and combustion of nonrenewable resources such as fossil fuels contribute significantly to air and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and habitat destruction. The release of pollutants from burning coal, oil, and natural gas not only degrades air quality but also leads to climate change and global warming. Moreover, the extraction of nonrenewable resources often involves destructive mining practices that disrupt ecosystems, contaminate water sources, and harm wildlife populations. By understanding the environmental consequences of relying on nonrenewable resources, we can strive to transition towards cleaner, more sustainable energy alternatives to mitigate these detrimental impacts on our planet’s health and well-being.
How can individuals and communities transition to using more renewable resources?
Transitioning to using more renewable resources is a crucial step for individuals and communities in building a sustainable future. One effective way to make this shift is by investing in renewable energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, and hydroelectric power. Individuals can also reduce their reliance on nonrenewable resources by adopting energy-efficient practices, promoting recycling initiatives, and supporting local sustainability efforts. Community-wide initiatives like implementing green building standards, establishing community gardens, and organizing educational programs can further encourage the transition to renewable resources. By taking proactive steps at both the individual and community levels, we can collectively work towards a greener and more sustainable world for generations to come.