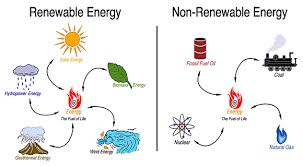
Non-Renewable Energy Sources Examples
Non-renewable energy sources are those that cannot be easily replenished within a short period of time. These energy sources are finite and contribute to environmental degradation. Here are some examples of non-renewable energy sources:
Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas are the most commonly used non-renewable energy sources. These fuels are formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals that have been buried and compressed over millions of years.
Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is generated by splitting atoms in a process called nuclear fission. This process releases a large amount of heat energy, which is used to generate electricity. While nuclear energy is considered clean in terms of greenhouse gas emissions, it produces radioactive waste that poses long-term environmental challenges.
Tar Sands
Tar sands, also known as oil sands, are a mixture of sand, water, clay, and bitumen (a thick form of petroleum). Extracting oil from tar sands is an energy-intensive process that has significant environmental impacts, including deforestation and water pollution.
Shale Gas
Shale gas is natural gas trapped within shale rock formations deep underground. The extraction of shale gas involves hydraulic fracturing (fracking), a controversial method that can lead to groundwater contamination and seismic activity.
In conclusion, while non-renewable energy sources play a significant role in meeting global energy demands, their use comes with environmental consequences. As we strive for a more sustainable future, transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power is essential to reducing our reliance on finite resources and mitigating climate change.
5 Key Insights About Non-Renewable Energy Sources and Their Impact
- Non-renewable energy sources include coal, oil, and natural gas.
- These energy sources are finite and will eventually run out.
- Burning non-renewable energy sources releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change.
- Exploration and extraction of non-renewable energy sources can have negative environmental impacts such as habitat destruction and water pollution.
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind can help reduce reliance on non-renewable resources.
Non-renewable energy sources include coal, oil, and natural gas.
Non-renewable energy sources encompass coal, oil, and natural gas, which are widely utilized for power generation and fuel production. These resources are finite in nature and their extraction and consumption contribute to environmental concerns such as air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and habitat destruction. As society seeks to transition towards more sustainable energy options, the limitations of non-renewable sources highlight the importance of investing in renewable alternatives to ensure a cleaner and more resilient future for generations to come.
These energy sources are finite and will eventually run out.
Non-renewable energy sources, such as fossil fuels, nuclear energy, tar sands, and shale gas, are finite resources that will eventually run out. As these sources are extracted and consumed at a rapid pace to meet global energy demands, the day will come when they are no longer available for use. This inevitability highlights the importance of transitioning to sustainable and renewable energy sources to ensure a reliable and environmentally friendly energy supply for future generations. By recognizing the finite nature of non-renewable energy sources, we can make informed choices that promote long-term energy security and environmental preservation.
Burning non-renewable energy sources releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change.
Burning non-renewable energy sources releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. The combustion of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas releases carbon dioxide and other pollutants that trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to global warming and climate disruptions. As we continue to rely on non-renewable energy sources for our electricity, transportation, and heating needs, we exacerbate the environmental challenges posed by climate change. Transitioning to renewable energy sources is crucial in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change on our planet.
Exploration and extraction of non-renewable energy sources can have negative environmental impacts such as habitat destruction and water pollution.
The exploration and extraction of non-renewable energy sources can have detrimental effects on the environment, including habitat destruction and water pollution. The process of locating and extracting fossil fuels or other non-renewable resources often involves disrupting natural ecosystems, leading to the loss of biodiversity and wildlife habitats. Additionally, activities like drilling or mining can result in the contamination of water sources, posing risks to both aquatic life and human health. It is crucial to consider these environmental impacts when evaluating the true cost of relying on non-renewable energy sources for our energy needs.
Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind can help reduce reliance on non-renewable resources.
Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind can play a crucial role in reducing our dependence on non-renewable resources. By harnessing the power of sunlight and wind, we can generate clean energy without depleting finite fossil fuel reserves or causing environmental harm. Embracing renewable energy technologies not only helps mitigate climate change but also fosters sustainable development and a greener future for generations to come.