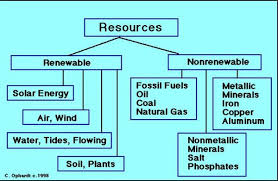
Non-Renewable Natural Resources: Understanding the Impact
Non-renewable natural resources are finite sources of energy and materials that cannot be replenished within a human lifetime or even over many lifetimes. These resources, such as fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas), minerals (iron, copper, gold), and nuclear fuels (uranium), play a crucial role in powering modern economies and industries.
However, the exploitation of non-renewable natural resources comes with significant environmental and social consequences. The extraction and burning of fossil fuels contribute to air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and climate change. Mining for minerals often leads to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water contamination.
As these resources become increasingly scarce and difficult to extract, the competition for access to them intensifies, leading to geopolitical tensions and conflicts. Moreover, the reliance on non-renewable resources poses risks to energy security and economic stability.
To address these challenges, it is essential to reduce our dependence on non-renewable natural resources and transition towards sustainable alternatives. Investing in renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower can help mitigate climate change and reduce environmental degradation.
Furthermore, adopting practices such as recycling, resource conservation, and efficient use of materials can help extend the lifespan of non-renewable resources and minimize waste generation. Embracing a circular economy model that focuses on reuse and regeneration can pave the way for a more sustainable future.
In conclusion, understanding the impact of non-renewable natural resources is crucial for making informed decisions about resource management and conservation. By promoting sustainability practices and embracing renewable alternatives, we can work towards safeguarding our planet for future generations.
Six Benefits of Non-Renewable Natural Resources for Energy and Economic Development
- Non-renewable natural resources provide a reliable and consistent source of energy for various industries and households.
- They have high energy density, making them efficient for power generation and transportation.
- Non-renewable resources are readily available in many regions, contributing to economic development and job creation.
- These resources have been essential in driving technological advancements and innovation across different sectors.
- Their abundance has historically supported global industrial growth and infrastructure development.
- Non-renewable natural resources can serve as a valuable export commodity, boosting trade balances and national economies.
7 Major Drawbacks of Relying on Non-Renewable Natural Resources
- Depletion of finite resources
- Contribution to air pollution
- Greenhouse gas emissions
- Climate change impact
- Habitat destruction from extraction
- Water contamination from mining activities
- Geopolitical conflicts over scarce resources
Non-renewable natural resources provide a reliable and consistent source of energy for various industries and households.
Non-renewable natural resources offer a significant advantage by providing a dependable and consistent source of energy for a wide range of industries and households. The reliability of non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels ensures that energy needs can be met consistently, supporting industrial processes, transportation systems, and daily activities in households. This stability in energy supply helps maintain economic productivity and societal functions, making non-renewable resources a crucial component of our current energy infrastructure.
They have high energy density, making them efficient for power generation and transportation.
Non-renewable natural resources possess a notable advantage in their high energy density, which renders them exceptionally efficient for power generation and transportation purposes. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, pack a significant amount of energy into a relatively small volume, allowing for the production of large amounts of electricity or the propulsion of vehicles over long distances with minimal resource consumption. This high energy density characteristic contributes to the reliability and effectiveness of non-renewable resources in meeting the energy demands of modern society, despite their environmental drawbacks.
Non-renewable resources are readily available in many regions, contributing to economic development and job creation.
Non-renewable natural resources, such as fossil fuels and minerals, offer a significant advantage in that they are often readily available in many regions around the world. The accessibility of these resources plays a crucial role in driving economic development and job creation within local communities. Extracting and utilizing non-renewable resources can stimulate industries, attract investments, and create employment opportunities in sectors like mining, energy production, and manufacturing. This steady influx of economic activity not only boosts regional prosperity but also supports infrastructure development and technological advancements, ultimately contributing to overall societal progress.
These resources have been essential in driving technological advancements and innovation across different sectors.
Non-renewable natural resources have played a pivotal role in propelling technological advancements and fostering innovation across various sectors. From the Industrial Revolution to the present day, fossil fuels, minerals, and nuclear fuels have been fundamental in powering industries, transportation systems, and infrastructure development. The energy density and versatility of non-renewable resources have enabled the creation of cutting-edge technologies, such as advanced machinery, electronics, and medical devices. By serving as the backbone of modern civilization’s progress, non-renewable natural resources have catalyzed innovation and propelled societies towards greater efficiency and productivity.
Their abundance has historically supported global industrial growth and infrastructure development.
The abundance of non-renewable natural resources has played a pivotal role in driving global industrial growth and infrastructure development throughout history. These resources, such as coal, oil, and minerals, have been essential in fueling industries, powering machinery, and constructing critical infrastructure like roads, buildings, and transportation networks. Their widespread availability has provided the foundation for economic progress and technological advancement on a global scale, enabling societies to expand and prosper by harnessing the energy and materials derived from non-renewable sources.
Non-renewable natural resources can serve as a valuable export commodity, boosting trade balances and national economies.
Non-renewable natural resources can play a pivotal role in enhancing trade balances and bolstering national economies as valuable export commodities. Countries rich in non-renewable resources such as oil, gas, or minerals can capitalize on these assets to generate significant revenue through exports. By tapping into global markets and meeting the demand for these resources, nations can strengthen their trade positions, attract foreign investments, and stimulate economic growth. The export of non-renewable natural resources presents a strategic opportunity for countries to diversify their economies and leverage their resource endowments to create sustainable development pathways.
Depletion of finite resources
The depletion of finite resources is a significant con associated with non-renewable natural resources. As these resources are extracted and consumed at a rapid pace, they are being depleted faster than they can be naturally replenished. This leads to scarcity, rising costs, and increased competition for access to these valuable resources. The depletion of finite resources not only threatens the availability of essential materials and energy sources but also contributes to environmental degradation and ecosystem disruption. Addressing this con requires a shift towards sustainable practices and the development of alternative, renewable sources of energy and materials to ensure a more secure and balanced future for generations to come.
Contribution to air pollution
The extraction and consumption of non-renewable natural resources, such as fossil fuels, significantly contribute to air pollution. When these resources are burned for energy production or transportation, they release harmful pollutants into the atmosphere, including carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These pollutants not only degrade air quality but also have detrimental effects on human health, leading to respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and other serious health issues. Addressing the con of air pollution from non-renewable natural resources is crucial for mitigating environmental damage and safeguarding public health.
Greenhouse gas emissions
The con of greenhouse gas emissions associated with non-renewable natural resources poses a significant threat to our environment and climate. The extraction, production, and consumption of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas release large quantities of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. These emissions trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures, melting ice caps, more frequent extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems. Addressing this con requires a shift towards renewable energy sources and sustainable practices to reduce our carbon footprint and mitigate the impact of greenhouse gas emissions on our planet.
Climate change impact
The extraction and consumption of non-renewable natural resources, particularly fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, contribute significantly to climate change. The burning of these resources releases greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, trapping heat and leading to global warming. This results in a range of adverse effects, including rising sea levels, more frequent and severe weather events, disruptions to ecosystems, and threats to human health. Addressing the climate change impact of non-renewable resources is crucial for mitigating environmental damage and transitioning towards a more sustainable energy future.
Habitat destruction from extraction
Habitat destruction resulting from the extraction of non-renewable natural resources poses a significant environmental con with far-reaching consequences. Mining and drilling activities often lead to the clearing of forests, disruption of ecosystems, and displacement of wildlife, causing irreparable damage to delicate habitats. The loss of biodiversity and disruption of ecological balance can have cascading effects on entire ecosystems, impacting not only local flora and fauna but also threatening the survival of endangered species. Addressing this con requires careful consideration of sustainable resource extraction practices and the implementation of stringent environmental regulations to minimize habitat destruction and protect our planet’s precious natural heritage.
Water contamination from mining activities
Water contamination from mining activities is a significant con of non-renewable natural resources exploitation. Mining operations can introduce harmful chemicals and heavy metals into water sources, contaminating groundwater and surface water bodies. This pollution poses serious risks to aquatic ecosystems, wildlife, and human health. The release of toxic substances such as lead, mercury, and arsenic can have long-lasting environmental consequences, impacting water quality and biodiversity. Efforts to mitigate water contamination from mining activities are essential to protect our precious water resources and ensure a sustainable future for all.
Geopolitical conflicts over scarce resources
Geopolitical conflicts over scarce non-renewable natural resources pose a significant challenge in today’s world. As countries compete for access to limited reserves of fossil fuels, minerals, and other vital resources, tensions rise, leading to power struggles, disputes, and even armed conflicts. The control and distribution of these resources become key factors in shaping international relations and influencing geopolitical alliances. Such conflicts not only threaten global stability but also exacerbate social injustice and economic disparities, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable resource management practices and the transition to renewable alternatives.