Ecosystem Ecology: Exploring the Interconnected Web of Life
Ecosystem ecology is a branch of ecology that focuses on studying the interactions between living organisms and their environment within a particular area. It delves into the intricate relationships between plants, animals, microorganisms, and their physical surroundings, examining how energy and nutrients flow through ecosystems.
One of the key concepts in ecosystem ecology is the idea of trophic levels, which represent different levels in a food chain or food web. Producers, such as plants and algae, convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores consume these producers, followed by carnivores that feed on herbivores. Decomposers break down organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil for producers to use again.
Energy flows through ecosystems in a unidirectional manner, with only a small fraction being transferred from one trophic level to the next. This flow of energy is essential for sustaining life within an ecosystem and maintaining its balance.
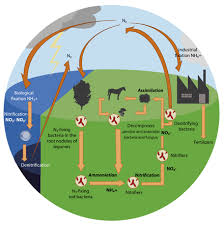
Furthermore, ecosystem ecology explores nutrient cycling processes such as the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and water cycle. These cycles are crucial for recycling essential elements needed for life and are influenced by both biotic (living organisms) and abiotic (non-living factors) components of an ecosystem.
Human activities have significantly impacted ecosystem dynamics through deforestation, pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change. Understanding ecosystem ecology is vital for devising sustainable management practices that preserve biodiversity and ecosystem services essential for human well-being.
In conclusion, ecosystem ecology provides valuable insights into the complex interactions that shape our natural world. By studying how organisms interact with each other and their environment, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnected web of life and work towards conserving our precious ecosystems for future generations.
Understanding Ecosystem Ecology: Key Questions and Insights
- What is ecosystem ecology?
- How do energy and nutrients flow through ecosystems?
- What are trophic levels in an ecosystem?
- Why are nutrient cycling processes important in ecosystem ecology?
- How do human activities impact ecosystem dynamics?
- What are some examples of ecosystem services provided by natural ecosystems?
- How can we apply the principles of ecosystem ecology to promote sustainability?
What is ecosystem ecology?
Ecosystem ecology is a specialized field within the broader study of ecology that focuses on understanding the intricate relationships between living organisms and their environment within a specific area. It delves into how energy and nutrients flow through ecosystems, examining the interconnected web of life that sustains diverse plant, animal, and microbial communities. By investigating trophic levels, nutrient cycling processes, and the impact of human activities on ecosystem dynamics, ecosystem ecology sheds light on the complex interactions that shape our natural world. Ultimately, it provides valuable insights into how we can better conserve and manage ecosystems for the benefit of all living organisms.
How do energy and nutrients flow through ecosystems?
Energy and nutrients flow through ecosystems in a dynamic and interconnected manner, driving the intricate web of life within these systems. Energy enters ecosystems primarily through sunlight, which is captured by producers like plants through photosynthesis. This energy is then transferred through trophic levels as organisms consume one another, with each transfer resulting in some energy loss as heat. Nutrients, on the other hand, cycle within ecosystems as they are taken up by plants, consumed by animals, and eventually returned to the environment through decomposition. These processes of energy flow and nutrient cycling are essential for maintaining the balance and sustainability of ecosystems, highlighting the interdependence of all living organisms within a given ecosystem.
What are trophic levels in an ecosystem?
Trophic levels in an ecosystem refer to the hierarchical levels within a food chain or food web where organisms occupy distinct positions based on their feeding relationships. These levels include producers, which convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis; herbivores, which consume producers; carnivores, which prey on herbivores; and decomposers, which break down organic matter. Each trophic level represents a step in the transfer of energy and nutrients through the ecosystem, highlighting the interconnected nature of species interactions and the flow of resources within an ecological community. Understanding trophic levels is essential for comprehending the dynamics of energy transfer and nutrient cycling that sustain life within ecosystems.
Why are nutrient cycling processes important in ecosystem ecology?
Nutrient cycling processes play a crucial role in ecosystem ecology as they are essential for the sustainability and functioning of ecosystems. These processes, such as the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and water cycle, involve the movement and exchange of nutrients between living organisms and their environment. Nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and others are recycled through these cycles, ensuring that they are available for plants, animals, and microorganisms to thrive. By efficiently recycling nutrients, ecosystem ecology maintains the balance of ecosystems, supports biodiversity, promotes plant growth, and sustains life within these intricate systems. Understanding and managing nutrient cycling processes is vital for preserving the health of ecosystems and safeguarding their ability to provide essential services for both nature and human societies.
How do human activities impact ecosystem dynamics?
Human activities have a profound impact on ecosystem dynamics through actions such as deforestation, pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change. Deforestation disrupts the balance of ecosystems by removing crucial habitats for plants and animals, leading to loss of biodiversity. Pollution from industrial and agricultural sources contaminates air, water, and soil, affecting the health of organisms within ecosystems. Habitat destruction due to urbanization and infrastructure development further diminishes available resources for wildlife, leading to population declines and ecosystem imbalances. Additionally, human-induced climate change alters temperature patterns, precipitation levels, and sea levels, causing disruptions in ecosystems worldwide. Understanding the detrimental effects of human activities on ecosystem dynamics is essential for implementing conservation efforts and sustainable practices to protect our planet’s delicate balance of life.
What are some examples of ecosystem services provided by natural ecosystems?
Natural ecosystems provide a wide range of essential ecosystem services that support life on Earth. Examples of these services include the regulation of climate through carbon sequestration and oxygen production by forests, the purification of water through wetlands and riparian zones, the pollination of crops by bees and other insects, and the control of pests by natural predators. Additionally, natural ecosystems offer cultural services such as recreational opportunities, aesthetic beauty, and spiritual value. These ecosystem services are vital for human well-being and highlight the interconnected relationship between nature and society.
How can we apply the principles of ecosystem ecology to promote sustainability?
Applying the principles of ecosystem ecology is essential in promoting sustainability by understanding and respecting the intricate relationships within natural systems. By embracing concepts such as energy flow, nutrient cycling, and biodiversity, we can design sustainable practices that mimic the resilience and efficiency of natural ecosystems. Implementing strategies like regenerative agriculture, green infrastructure development, and ecosystem restoration projects allows us to enhance ecosystem services, conserve resources, and minimize environmental impacts. By integrating the wisdom of ecosystem ecology into our decision-making processes, we can foster a harmonious balance between human activities and the natural world, ensuring a healthier planet for current and future generations.